Necessary Technical Skills for Aspiring Zoologists

Zoology, the scientific study of animal life, is an exciting and dynamic field that combines passion for wildlife with technical expertise. Aspiring zoologists often find themselves immersed in diverse ecosystems, from tropical rainforests to marine habitats. To excel in this challenging domain, one must master several essential technical skills. Let’s delve into these skills and their importance in modern zoology.
Understanding the Role of Technical Skills in Zoology
In the realm of zoology, technical skills act as the bridge between theoretical knowledge and real-world applications. Whether studying animal behavior, conserving endangered species, or developing biodiversity strategies, these skills are indispensable.
The field of zoology has evolved significantly over time. No longer limited to observing animals in their natural habitats, zoologists now employ cutting-edge tools and methods to analyze and interpret data. To keep pace with this progress, acquiring a strong foundation in technical skills is vital.
Essential Technical Skills for Zoologists
Proficiency in Scientific Research and Data Analysis
Zoologists are primarily scientists, which means research is at the core of their work. An essential technical skill for zoologists is the ability to design, execute, and analyze scientific studies.
- Field Data Collection: Techniques like GPS tracking, camera trapping, and acoustic monitoring are widely used. Zoologists must understand how to set up these tools effectively to gather accurate data.
- Statistical Analysis: Software such as R, SPSS, or Python helps zoologists process large datasets, draw meaningful conclusions, and publish findings.
The combination of field data and statistical tools allows zoologists to provide scientifically backed insights into animal behavior and ecosystem dynamics.
Knowledge of Geographic Information Systems (GIS)
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is crucial for mapping animal habitats, migration patterns, and population distributions. Zoologists frequently use GIS to overlay spatial data with environmental variables to understand habitat use.
For instance:
- Tracking endangered species like sea turtles across ocean currents.
- Studying the impact of deforestation on primate populations.
GIS helps in conservation planning, creating predictive models, and even identifying high-priority areas for biodiversity protection.
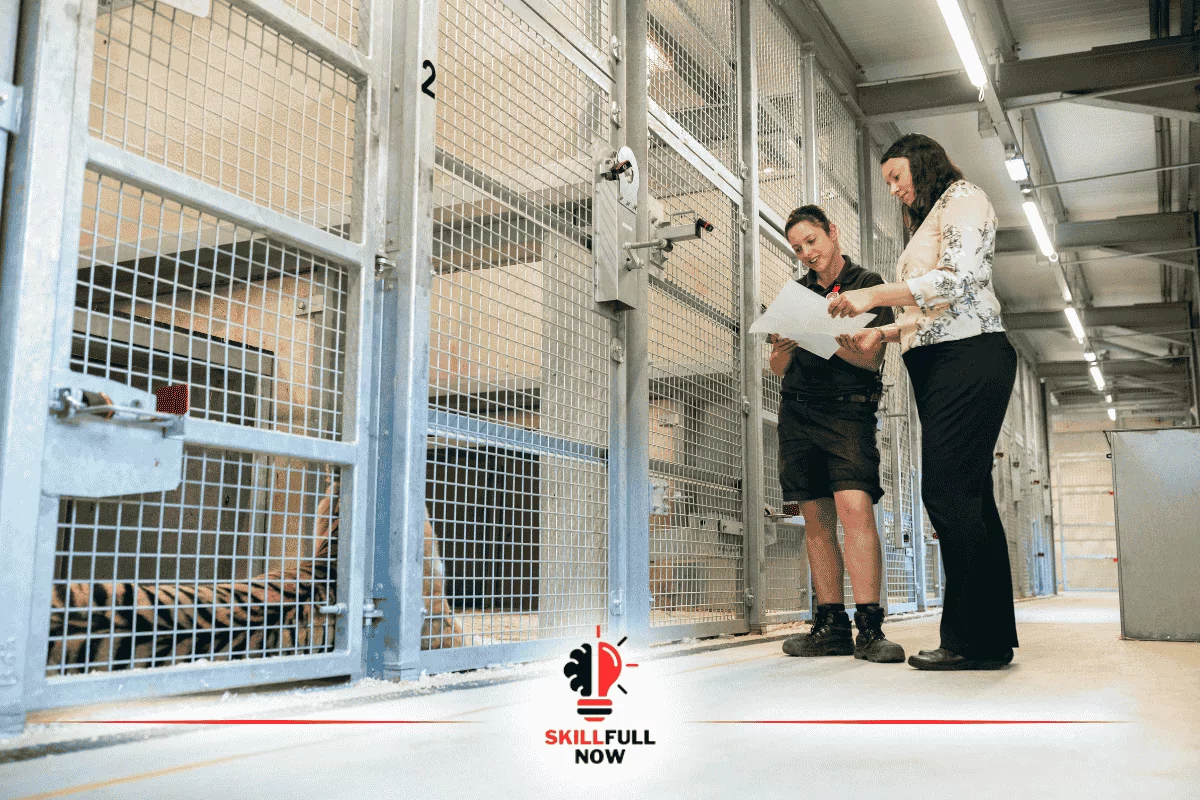
Skill in Animal Handling and Identification
Fieldwork often involves direct interactions with animals, making animal handling a critical skill for zoologists. Safety, both for the researcher and the animal, must always come first.
Key Techniques Include:
- Using nets, traps, or anesthetics responsibly to capture specimens.
- Properly tagging and releasing animals to study behavior or migration.
In addition, zoologists must possess strong identification skills, enabling them to classify species accurately, whether through morphology or genetic markers.
Understanding Molecular Biology and Genetics
Molecular biology has become a game-changer in zoology. Techniques such as DNA barcoding and genome sequencing provide invaluable insights into evolutionary relationships, genetic diversity, and species identification.
For example:
- Studying the genetic diversity of an endangered species can inform conservation strategies.
- Identifying cryptic species that are visually indistinguishable but genetically distinct.
A solid grasp of molecular tools is essential for modern zoologists to remain competitive in their field.
Technical Skills for Wildlife Conservation Efforts
Competency in Remote Sensing Technology
Remote sensing tools, such as drones and satellite imagery, are increasingly used in wildlife studies. These technologies allow zoologists to monitor habitats from afar, reducing disturbance to animals.
Applications Include:
- Mapping deforestation and its impact on biodiversity.
- Monitoring migration routes of large mammals like elephants.
Mastering these tools enhances efficiency and precision in conservation efforts.
Behavioral Observation Techniques
Understanding animal behavior requires patience and a keen eye for detail. Behavioral observation is a core skill for zoologists and involves documenting actions, interactions, and routines of species in their natural environment.
Important Tools for Behavioral Studies:
- Ethograms to record specific actions.
- Time-lapse cameras to capture nocturnal activity.
These methods help zoologists uncover patterns in feeding, mating, and territorial behavior, providing critical insights into ecosystem functioning.
Soft Skills That Complement Technical Expertise
While technical skills are vital, soft skills play an equally significant role in the success of a zoologist.
Team Collaboration
Zoology projects often involve working with interdisciplinary teams, including ecologists, geographers, and conservationists. Strong communication and collaboration skills ensure smooth project execution.
Problem Solving Abilities
Fieldwork rarely goes as planned. Adaptability and problem solving are essential when dealing with unforeseen challenges, such as equipment failure or adverse weather conditions.
Emerging Skills for Future Zoologists
AI and Machine Learning Applications
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing data processing in zoology. Zoologists use AI to analyze vast datasets, such as identifying individual animals in a population through image recognition.
Citizen Science Engagement
Involving local communities in data collection is an emerging trend. Skills in public engagement and education are invaluable for zoologists looking to broaden their impact.
The Importance of Continuous Learning
Zoology is a field where innovation happens rapidly. Staying updated on new technologies, methodologies, and research trends ensures a competitive edge. Enrolling in workshops, conferences, and online courses can help zoologists refine their skills continually.
Conclusion
The path to becoming a successful zoologist is paved with a mix of passion and technical skills. Mastering data analysis, GIS, molecular biology, and behavioral observation equips zoologists to tackle modern challenges in wildlife conservation and research. As the field evolves, staying adaptable and continuously learning new skills will be the key to success. By embracing technology and innovation, zoologists can make a lasting impact on our understanding of the natural world.
FAQs
What role does technology play in modern zoology?
Technology enhances the accuracy, efficiency, and scope of zoological research, from data collection to analysis and conservation planning.
Why is GIS important for Aspiring Zoologists?
GIS enables the mapping and analysis of animal habitats and migration patterns, aiding conservation and ecological studies.
Can soft skills impact a zoologist’s career?
Absolutely. Skills like teamwork, communication, and problem-solving are crucial for effective collaboration and successful projects.
How can aspiring Necessary Technical Skills for Aspiring Zoologists?
Participating in internships, fieldwork, and specialized courses can help build Necessary Technical Skills in Zoologists.
What are some common tools used by zoologists?
Tools like GPS devices, drones, GIS software, and molecular biology kits are widely used in zoological research.
How is AI influencing Necessary Technical Skills for Aspiring Zoologists?
AI simplifies data analysis, aids in species identification, and automates repetitive tasks, allowing zoologists to focus on deeper insights.





Hi, I wanted to know your price.
Ndewo, achọrọ m ịmara ọnụahịa gị.